An Introduction to Kali Linux for Cybersecurity Students
Kali Linux is a Debian-based Linux distribution designed specifically for penetration testing and security auditing. It is widely used by cybersecurity professionals, ethical hackers, and IT security teams for a variety of purposes, including vulnerability assessment, penetration testing, and digital forensics.
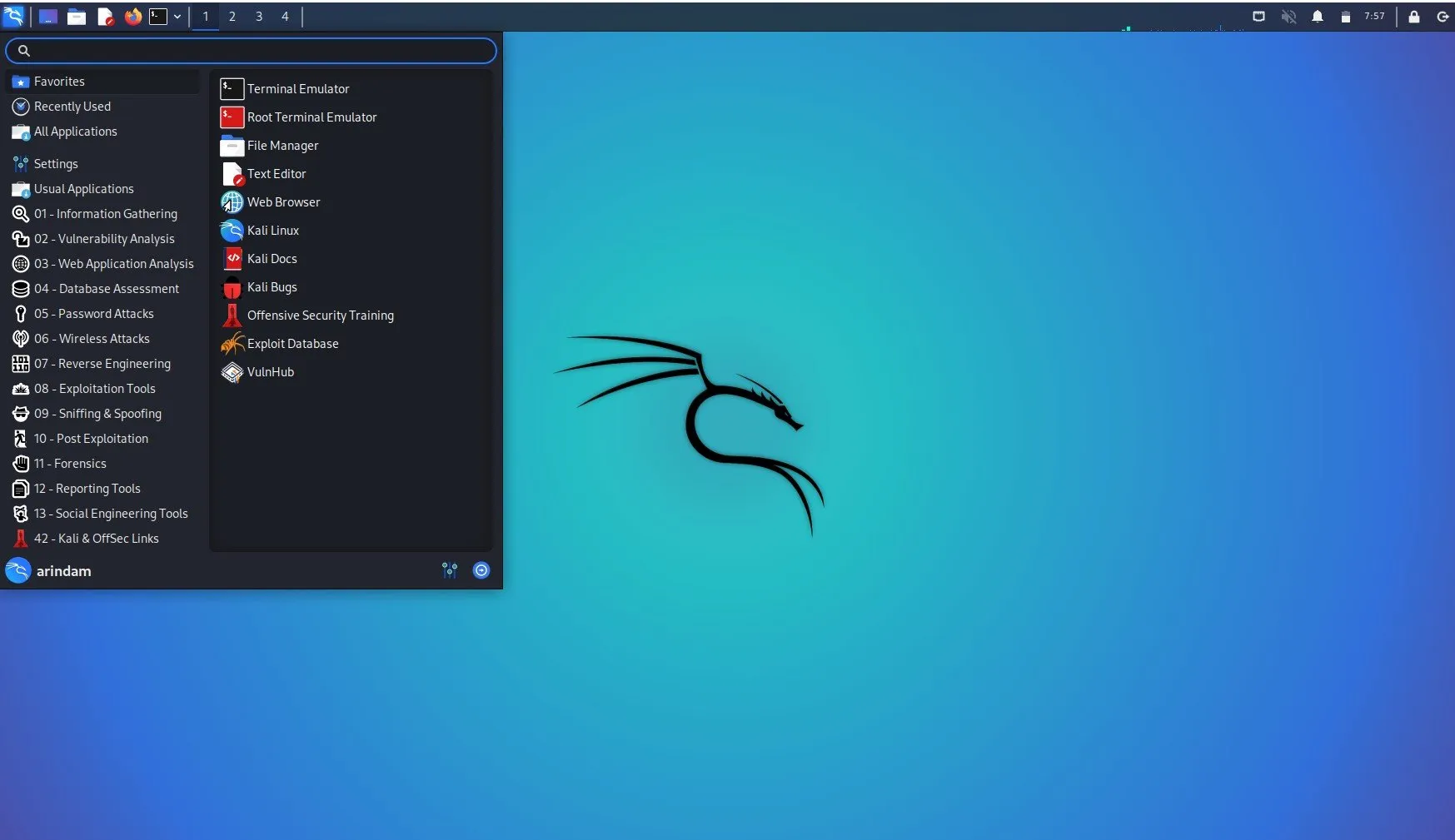
Key Features of Kali Linux
- Pre-installed Security Tools:
- Metasploit: A powerful exploitation framework used for developing and executing exploit code against a remote target machine.
- Nmap: A network scanning tool used for network discovery and security auditing.
- Wireshark: A network protocol analyzer used for network troubleshooting, analysis, and communications protocol development.
- John the Ripper: A password cracking tool.
- Burp Suite: A web vulnerability scanner.
- Aircrack-ng: A suite of tools to assess Wi-Fi network security.
- Over 600 penetration testing tools pre-installed.

- Customizability:
- Kali Linux can be customized based on the user’s needs. It supports a wide range of desktop environments such as GNOME, KDE, and Xfce.
- Free and Open Source:
- It is available free of cost and is open source, meaning its source code is available for anyone to examine, modify, and enhance.
- Wide Hardware Support:
- Kali Linux supports a wide range of hardware platforms, including ARM devices like Raspberry Pi, ensuring flexibility in deployment.
- Live Boot Capability:
- It can be booted as a live CD or live USB, which allows you to run the operating system without installing it on a hard drive. This is particularly useful for forensic analysis and situations where you don’t want to make any changes to the existing system.
- Regular Updates and Community Support:
- Kali Linux is actively maintained and regularly updated to include the latest security tools and patches. It also has a robust community that contributes to its development and provides support.
Installation and Use
- Installation Methods:
- Live Boot: Running directly from a CD, DVD, or USB without installing on the hard drive.
- Installation: Can be installed on a hard drive, virtual machine, or ARM device.
- Dual Boot: Can be set up alongside another operating system like Windows.
- Usage:
- Penetration Testing: Ethical hackers use Kali Linux to identify and exploit vulnerabilities in systems.
- Security Auditing: Organizations use it to audit their security posture and ensure compliance with security standards.
- Digital Forensics: Investigators use it for data recovery, analysis, and to gather digital evidence.
Learning Resources
- Official Documentation: Kali Linux has extensive documentation available on its official website.
- Books: Books like “Kali Linux Revealed” provide in-depth knowledge about the OS.
- Online Courses and Tutorials: Platforms like Udemy, Coursera, and YouTube offer various courses on using Kali Linux.
- Forums and Communities: Engage with other users and experts on forums like the Kali Linux Forums, Reddit, and Stack Exchange.
Getting Started
- Download: You can download the latest version of Kali Linux from the official Kali Linux website.
- Set Up a Virtual Environment: For beginners, setting up Kali Linux on a virtual machine (using tools like VirtualBox or VMware) is recommended. This allows you to experiment without affecting your primary OS.
- Basic Command Line Skills: Familiarize yourself with basic Linux commands as most of the tools and operations in Kali Linux are command-line based.
- Explore and Experiment: Start exploring the pre-installed tools and try to understand their purpose and functionality.
Kali Linux is a powerful tool for cybersecurity professionals, and learning to use it effectively can greatly enhance your skills in the field of cybersecurity.