
Google Authenticator Update: The Ultimate Guide to Enhanced Two-Factor Codes and Installation
The Game-Changing Update to Google Authenticator: Revolutionizing Two-Factor Authentication
In recent years, cybersecurity has become an increasingly critical concern, with online threats and data breaches on the rise. To address this, Google Authenticator, a widely used two-factor authentication (2FA) app, has undergone a transformative update that promises to enhance security and convenience for users. This article delves into the details of the Google Authenticator update, how it works, and the advantages it brings to the table. Additionally, we will guide you through the process of installing Google Authenticator.
Understanding Google Authenticator:
Google Authenticator is a free mobile app developed by Google, designed to add an extra layer of security to user accounts. It utilizes 2FA, a widely adopted security method that combines something you know (your password) with something you have (a unique verification code) to ensure your identity and protect against unauthorized access.
How Google Authenticator Works:
When setting up Google Authenticator, users link their online accounts, such as email, social media, or cloud storage, to the app by scanning a QR code or manually entering a provided code. Once linked, the app generates time-based, one-time passcodes (OTP) that users must enter during the login process, in addition to their regular password. These OTPs are valid for a short period, typically 30 seconds, before expiring.
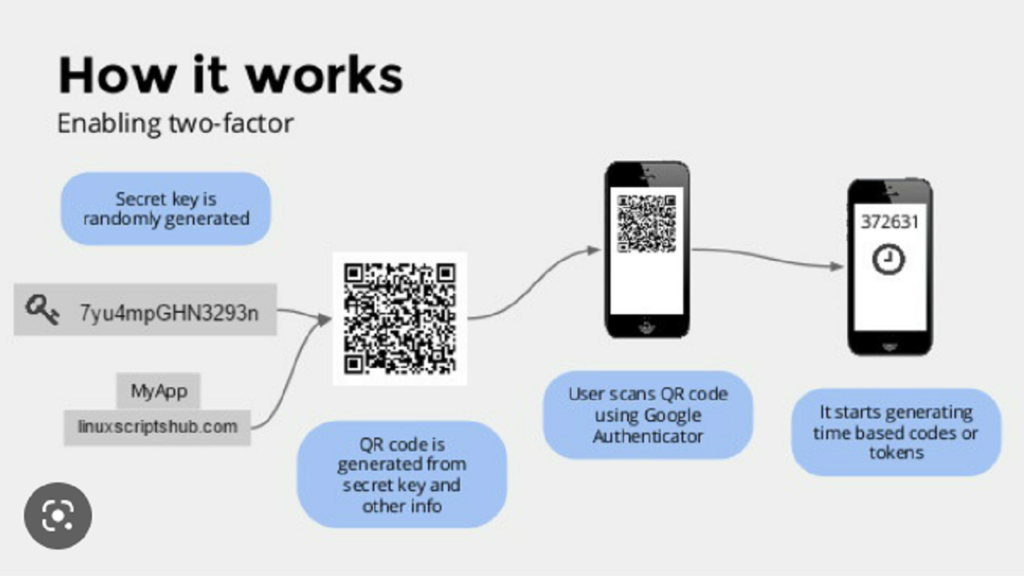
Advantages of Google Authenticator:
Enhanced Security: Google Authenticator adds an extra layer of security to your online accounts, making them significantly more resistant to unauthorized access. Even if a hacker obtains your password, they would still need access to your mobile device to obtain the time-based OTP, making the account more secure.
Offline Usage: Unlike some other 2FA methods, Google Authenticator works offline, making it accessible even in areas with limited internet connectivity. This makes it very convenient for travelers or in situations where a stable internet connection is not available.
Multi-Account Support: Google Authenticator allows users to manage multiple accounts within a single app, eliminating the need for separate authentication apps for each service. This streamlines the process and reduces app clutter on your device.
Easy Setup: The setup process for Google Authenticator is straightforward. By scanning the QR code or manually entering the provided code, users can quickly link their accounts to the app. This simplicity makes it accessible to a wide range of users, including those who may not be highly tech-savvy.
Installing Google Authenticator:
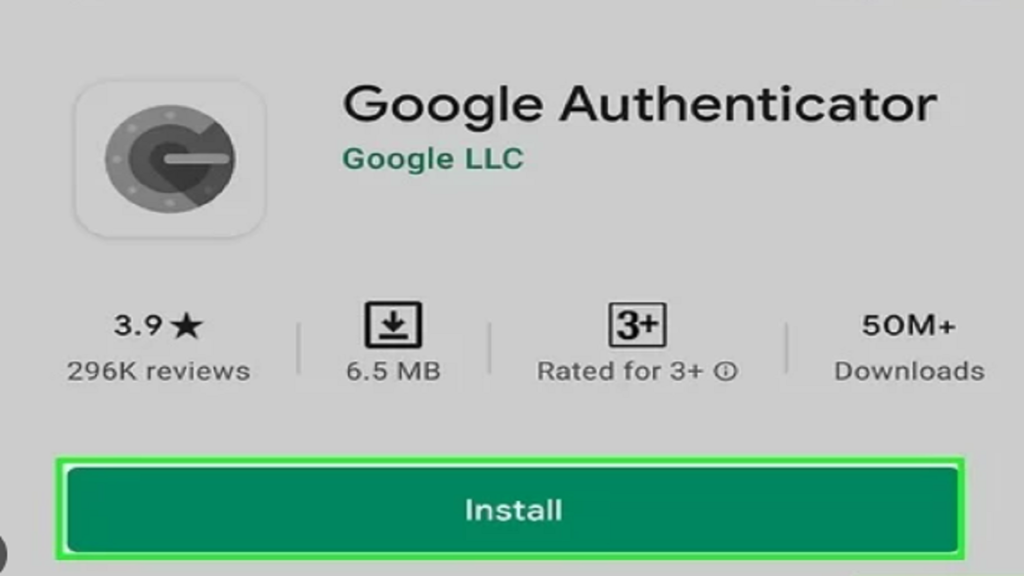
Download: Google Authenticator is available for both Android and iOS devices. Go to the respective app store (Google Play Store or Apple App Store) and search for “Google Authenticator.” Tap on the app and select “Install” or “Get” to download and install it on your device.
Setup: Open the app and follow the on-screen instructions to set up Google Authenticator. You may choose to scan a QR code provided by the service you wish to link, or manually enter the provided code.
Backup: It is essential to create a backup for your Google Authenticator app. Some services provide backup codes during setup that you can save securely in case your device is lost or reset. Alternatively, you can use an authenticator app that supports cloud backup, such as Authy or LastPass Authenticator.
Verification: After setup, the app will generate time-based OTPs for your linked accounts. During the login process, you will be prompted to enter the verification code displayed in Google Authenticator alongside your regular password.
The recent update to Google Authenticator represents a significant advancement in securing online accounts with the introduction of two-factor authentication. By adding an extra layer of protection through time-based OTPs, Google Authenticator enhances security while offering ease














I don’t think the title of your article matches the content lol. Just kidding, mainly because I had some doubts after reading the article.